Organization
Training organization
The Master's degree is organized into 4 semesters (S1 to S4), structured into compulsory or elective TU (teaching units). Each TU has a value in credits (ECTS). Each semester is worth 30 ECTS. The Master's degree is awarded on completion of 120 ECTS.
Prolegomena
Due to the highly heterogeneous nature of the populations recruited, the first year starts a fortnight earlier than theM2. These two weeks are then used to introduce students to the basic skills that will be considered acquired in the specialization's teaching units. Although they are not associated with any ECTS credits, theMaths, Electronics, Biology and Health prolegomena are nevertheless compulsory, enabling students to self-assess the requirements they will be asked to meet later on. By way of example, the Mathematics prolegomena are structured around three main themes: complex numbers, linear algebra and analysis (differentiation, integration and differential equations), which will find their respective applications in specific courses on Sensors or Robotics.
M1: First year of Master
- S1: First semester
Given the heterogeneity of the curricula followed by students recruited to the first year of the TecSan specialization, two specific courses are offered. The first enables students with a basic knowledge of electronics to supplement their knowledge through certain teaching units taken jointly with the Master EEA(https://www.eea.univ-montp2.fr). These include, in particular, "Analog Electronics" and "Signal Acquisition and Processing". Similar courses are offered to students from the Biology and Health streams, but with an adapted pedagogical approach. Reinforced by a module entitled "Mathematics / Statistics / Data Analysis", these courses form the first scientific part of the curriculum. At the same time, the program is complemented by specific health-related courses given to the entire graduating class at the Montpellier Faculty of Medicine. These are: "Health structures and issues" and "Scope of application of ICT in HEALTH". The latter takes the form of lectures/debates given every Tuesday evening by national healthcare professionals. Videos of these evenings can be viewed on the course website(https://www.telecom-montpellier.fr). - S2: Second semester
The second semester is also the last one, during which the class is divided into specific courses, offering a differentiated approach to Image, Sensors or Robotics.
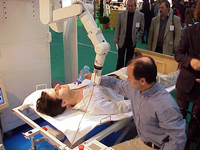
Medical RoboticsPhilippe Poignet

Epimysial electrode (copyrights SUAWproject), D. Guiraud
Radiation from an ultrasonicsensor, E. Le Clézio
Students are then offered a degree of specialization through a choice of two teaching units on "Medical Robotics", "Neuro-Prosthetics" or "Sensors for the Medical Sector". A 3 to 4 month internship in a research laboratory, healthcare facility or company completes the first year.
M2: Second year of Master
After the first year of specialized courses, students follow the same curriculum in the second year of the Master's program.
- S3: First semester
The UEs of the first semester of the second year are devoted to reinforcing the specialty modules covered in M1. These are "Sensors and Instrumentation", "Modeling/Regulation" and "Microfabrication/Microfluidics".
To enable students to pursue the specialization of some of their skills begun in the first year, two UEs are also available to choose from: "Medical Robotics 2", "Neuroprosthesis 2" and "IR Thermography & Optical Detectors". - S4: Second semester
The final semester of the Master's program is devoted to professionalization, with courses in industryTU Business Knowledge/Legal and Ethics) and researchTU Bibliographic Analysis/Scientific Journals). The program ends with a 4-6 month internship in a company, hospital or laboratory.
Professionally-oriented teaching units
The "Health Devices Engineering" specialization of the "Sciences and Digital Health" Master's degree is structured around professionalizing teaching units designed to provide students with a sound knowledge of the industrial or academic environment, depending on their career objectives.
Over the two years of the Master's program, four professionalization courses are offered in the form of projects (or discontinuous internships) corresponding to three half-days per week from the beginning of October to the end of March, which can be continued by three- to six-month internships at the end of each year. Depending on their choices and the opportunities available, students can have access to four different institutions, thus gaining diversified experience or, on the contrary, specializing over the two years in a particular field.
The following list presents a sample of the projects and/or internships carried out by IDS students:
- Methods for characterizing the properties of blood: Study of the coagulation phenomenon,
- Feasibility study of characterizing the viscoelastic properties of blood before and during the coagulation cascade using ultrasound methods,
- Study of intra- and postoperative cardiac distress,
- Instrumentation for studying the effect of mechanical stress on stem cell differentiation,
- Production of micro-fluidic circuits for cell culture,
- Yeast cell culture in micro-fluidic circuits ,
- Creation of nanofluidic circuits for DNA combing,
- Functional electrical stimulation,
- Curcumin, an insulin-stimulating plant substance of interest,
- Search for markers of functional asymmetries in the case of lateralized fatigue,
- Programming in C language of the interface of an endoscope holder dedicated to endoscopic sinus and skull base surgery.
Most of these professional training courses take place in research laboratories at the University of Montpellier or in industry.
Description of teaching units
The teaching unitsTU) presented below correspond to the LMD5 model valid from September 2021.
M1- Health Device Engineering (HDE)
Semester 7 :
Prolegomena in Mathematics (1 ECTS)
Introduction to Electronics (1 ECTS)
Healthcare structures and issues (4 ECTS)
Conferences on medicine and ICT (2 ECTS)
Health economics and organization (2 ECTS)
Engineering : Mathematics (4 ECTS)
Engineering : Computer Science (4 ECTS)
Semester 8 :
Health: Chronic diseases and innovation (2 ECTS)
Signal Acquisition and Processing (3 ECTS)
US sensors for biomedical applications (3 ECTS)
Sensors and image processing (4 ECTS)
1 TU to choose from
Neuroprosthesis 1 (4 ECTS)
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence - Data analysis (4 ECTS)
M2- Health Device Engineering (HDE)
Semester 9 :
Introduction to business and research (2 ECTS)
Bibliographic analysis and scientific watch (2 ECTS)
Professionalization: R&D operations (2 ECTS)
Health: Physical Activity (5 ECTS)
Data acquisition and signal processing for biomedical applications (5 ECTS)
1 TU to choose from
Neuroprosthesis 2 (4 ECTS)
Data analysis (4 ECTS)
Artificial Intelligence (4 ECTS)